前言:
本文适用于javaer,其他开发者或许可以借鉴。
写本文的主旨有两个,一是简单的给大家介绍下单元测试,二是通过一个简单的示例来介绍一些单元测试的技巧,希望以此来降低大家写单元测试的门槛。
1、单元测试的定义
单元测试通常是由软件开发人员编写和运行的自动化测试,以确保应用程序的一部分(称为“单元”)符合其设计并按预期运行。在过程编程中,一个单元可以是一个完整的模块,但更常见的是一个单独的函数或过程。在面向对象编程中,一个单元通常是一个完整的接口,例如一个类,或者一个单独的方法。通过首先为最小的可测试单元编写测试,然后是它们之间的复合行为,可以为复杂的应用程序构建全面的测试。
Unit tests are typically automated tests written and run by software developers to ensure that a section of an application (known as the “unit”) meets its design and behaves as intended. In procedural programming, a unit could be an entire module, but it is more commonly an individual function or procedure. In object-oriented programming, a unit is often an entire interface, such as a class, or an individual method. By writing tests first for the smallest testable units, then the compound behaviors between those, one can build up comprehensive tests for complex applications.
——Wikipedia, Unit testing
简单来说,单元测试是针对一个单元编写测试方法。其中的单元可以是一个很单纯的函数,也可以是一个完整的接口,该接口中可以包含各种其他函数的调用。
2、单元测试用例
该项目的 SpringBoot 版本是 2.2.5.RELEASE。
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starters</artifactId>
<version>2.2.5.RELEASE</version>
</parent>➮ 2-1.项目文件准备
假设有项目文件的目录结构如下:

java-study-web-provider 依赖 java-study-web-api, java-study-common-provider
java-study-web-api 依赖 java-study-common-api
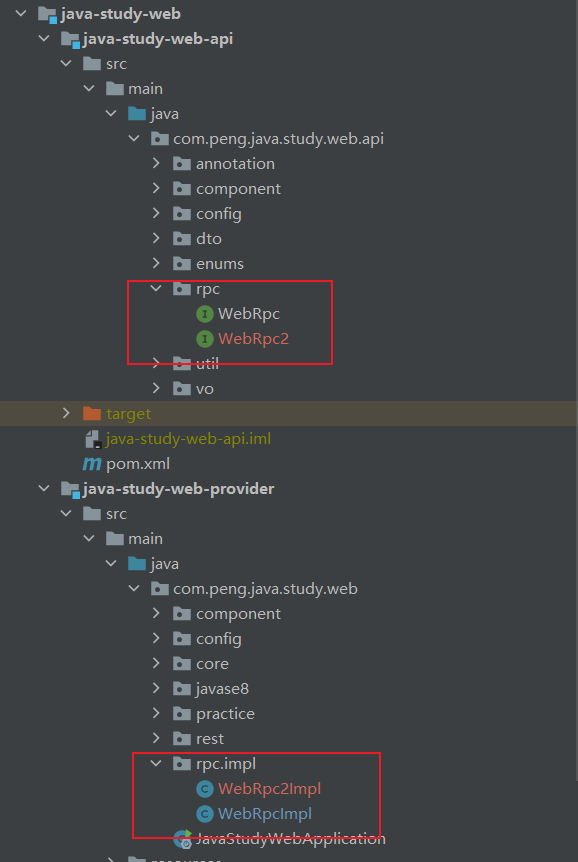
java-study-common-provider 依赖 java-study-web-api, java-study-common-api在 java-study-web-api 包中有个rpc 包,其中有两个 rpc 接口,分别是
WebRpc.class & WebRpc2.class。然而,这两个接口的实现类在 java-study-web-provider 包中。
public interface WebRpc {
ApiResult<String> get();
ApiResult<String> get2(String param);
}public interface WebRpc2 {
ApiResult<String> get();
ApiResult<String> get(String param);
}@Service
public class WebRpcImpl implements WebRpc {
@Override
public ApiResult<String> get() {
return ApiResult.success("get success");
}
@Override
public ApiResult<String> get2(String param) {
return ApiResult.success(param);
}
}@Service
public class WebRpc2Impl implements WebRpc2 {
@Override
public ApiResult<String> get() {
return ApiResult.success("get success");
}
@Override
public ApiResult<String> get(String param) {
return null;
}
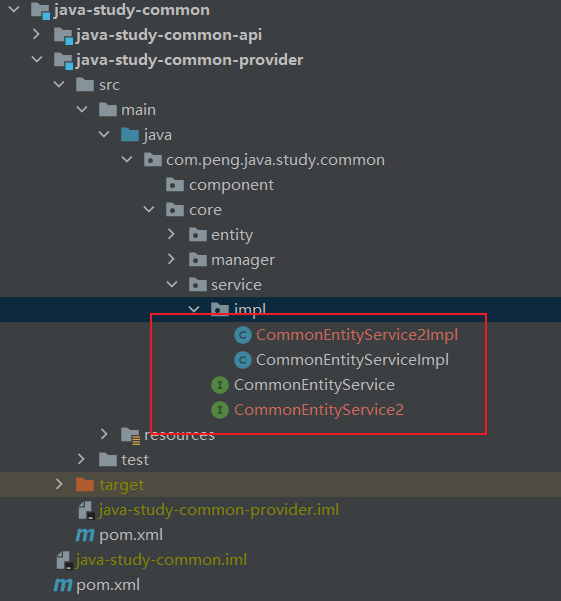
}在 java-study-common-provider 包中有个 service 包,其中有两个 service 接口以及对应的实现类,分别是 CommonEntityService.class, CommonEntityService2.class, CommonEntityServiceImpl.class, CommonEntityService2Impl.class,在两个实现类中都有引用 rpc 接口。
public interface CommonEntityService {
ApiResult<Void> test(CommonEntity commonEntity);
}public interface CommonEntityService2 {
}@Service
public class CommonEntityServiceImpl implements CommonEntityService {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Autowired
private CommonEntityManager commonEntityManager;
@Autowired
private WebRpc webRpc;
@Override
public ApiResult<Void> test(CommonEntity commonEntity) {
// webRpc 单元测试时可能为null
ApiResult<String> getRpc = webRpc.get();
if (!getRpc.getSuccess()) {
logger.info("getRpc fail: {}", getRpc);
return ApiResult.error(getRpc);
}
ApiResult<String> getRpc2 = webRpc.get2("test");
if (!getRpc2.getSuccess()) {
logger.info("getRpc2 fail: {}", getRpc2);
return ApiResult.error(getRpc2);
}
// 依赖远程方法调用结果
Optional<String> remoteResultOpt = RmiUtil.getRemoteResult();
if (!remoteResultOpt.isPresent()) {
logger.info("getRemoteResult fail");
return ApiResult.error(BizRespStatusEnum.SYS_ERR);
}
// 入库
int insertNo = commonEntityManager.insert(commonEntity);
logger.info("insert {} common entity", insertNo);
return ApiResult.success(null);
}
}@Service
public class CommonEntityService2Impl implements CommonEntityService2 {
@Autowired
private WebRpc2 webRpc2;
}➮ 2-2.针对 CommonEntityService.class 编写单元测试
先加入 SpringBootTest 依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>创建对应的单元测试类。
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = CommonTestApplication.class)
public class CommonEntityServiceTest {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Autowired
private CommonEntityService commonEntityService;
@Test
public void test() {
ApiResult<Void> testSuccess = commonEntityService.test(new CommonEntity());
Assert.isTrue(testSuccess.getSuccess(), "testSuccess fail");
logger.info("testSuccess: {}", JSON.toJSONString(testSuccess));
}
}当我们去执行单元测试的 test() 方法时,会出现 NoSuchBeanDefinitionException 异常。
Caused by: org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type 'com.peng.java.study.web.api.rpc.WebRpc2' available: expected at least 1 bean which qualifies as autowire candidate. Dependency annotations: {@org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired(required=true)}
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:1695)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.doResolveDependency(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:1253)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.resolveDependency(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:1207)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor$AutowiredFieldElement.inject(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:640)
... 43 more这是因为我们执行单元测试的这个模块虽然依赖了 java-study-web-api 包,能够调用 rpc 方法,但是没有依赖 java-study-web-provider 包,没办法注入对应的实现类。 有3种方法可以解决这个问题:
I.将该单元测试类挪到 java-study-web-provider 包中,这样就能加载到所有的 bean 了。 这个方法有局限性,每次执行单元测试都需要加载所有模块的文件,大大的降低了单元测试的效率。
II .在注入rpc的注解 @Autowired 上加上 required = false
@Autowired(required = false)
private WebRpc2 webRpc2;这个方法有局限性,假设每次新增的 service 类都需要注入同一个 rpc 时,那每个 rpc 的注解 @Autowired 都需要使用 required = false,不然就没办法启动单元测试,由此可见是比较麻烦的。
III.使用Mock,在执行单元测试前,将依赖但又没办法获取到实现类的 bean 注入进去。
将mokito包加入项目。
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mockito/mockito-inline -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mockito</groupId>
<artifactId>mockito-inline</artifactId>
<version>4.5.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mockito/mockito-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mockito</groupId>
<artifactId>mockito-core</artifactId>
<version>4.5.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/net.bytebuddy/byte-buddy-agent -->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.bytebuddy</groupId>
<artifactId>byte-buddy-agent</artifactId>
<version>1.12.9</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/net.bytebuddy/byte-buddy -->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.bytebuddy</groupId>
<artifactId>byte-buddy</artifactId>
<version>1.12.8</version>
</dependency>
使用 @MockBean 和 MockitoAnnotations.openMocks(this) 可以将依赖的 bean 注入进去。
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = CommonTestApplication.class)
public class CommonEntityServiceTest {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Autowired
private CommonEntityService commonEntityService;
@MockBean
public WebRpc webRpc;
@MockBean
public WebRpc2 webRpc2;
@BeforeEach
public void before(){
MockitoAnnotations.openMocks(this);
}
@Test
public void test() {
ApiResult<Void> testSuccess = commonEntityService.test(new CommonEntity());
Assert.isTrue(testSuccess.getSuccess(), "testSuccess fail");
logger.info("testSuccess: {}", JSON.toJSONString(testSuccess));
}
}此时再执行 test() 方法,不再出现 NoSuchBeanDefinitionException 异常,但会出现 NullPointerException 异常。这是因为我们虽然注入了 bean,但是这个bean是个空的,因此在 commonEntityService.test 方法中执行 webRpc.get() 时,会报 NullPointerException 异常。 为解决这个问题,我们可以继续使用 mock,Mockito.when(). thenReturn()。
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = CommonTestApplication.class)
public class CommonEntityServiceTest {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Autowired
private CommonEntityService commonEntityService;
@MockBean
public WebRpc webRpc;
@MockBean
public WebRpc2 webRpc2;
@BeforeEach
public void before(){
MockitoAnnotations.openMocks(this);
}
@Test
public void test() {
Mockito.when(webRpc.get()).thenReturn(ApiResult.success("mock result 1"));
Mockito.when(webRpc.get2("test")).thenReturn(ApiResult.success("mock result 2"));
ApiResult<Void> testSuccess = commonEntityService.test(new CommonEntity());
Assert.isTrue(testSuccess.getSuccess(), "testSuccess fail");
logger.info("testSuccess: {}", JSON.toJSONString(testSuccess));
}
}
再次执行 test() 方法,此时执行已经成功了,打印日志如下所示。
2022-05-21 22:23:23.094 INFO 3760 --- [ main] c.p.j.s.c.c.s.i.CommonEntityServiceImpl : insert 0 common entity
2022-05-21 22:23:23.161 INFO 3760 --- [ main] c.p.j.s.c.c.s.CommonEntityServiceTest : apiResult: {"code":"200","msg":"调用成功","success":true}虽然已经成功执行了单元测试,但如果需要 mock 的 bean 很多的话,那不是每个测试类都需要写一遍 mock,很浪费时间啊,因此,我们可以把需要 mock 的 bean 全都放到一个类中进行管理。
@Component
public class CommonMockFactory {
@BeforeEach
public void before(){
MockitoAnnotations.openMocks(this);
}
@MockBean
public WebRpc webRpc;
@MockBean
public WebRpc2 webRpc2;
}
然后在需要单元测试的类中进行注入即可。
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = CommonTestApplication.class)
public class CommonEntityServiceTest {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Autowired
private CommonEntityService commonEntityService;
@Autowired
private CommonMockFactory commonMockFactory;
@Test
public void test() {
Mockito.when(commonMockFactory.webRpc.get()).thenReturn(ApiResult.success("mock result 1"));
Mockito.when(commonMockFactory.webRpc.get2("test")).thenReturn(ApiResult.success("mock result 2"));
ApiResult<Void> testSuccess = commonEntityService.test(new CommonEntity());
Assert.isTrue(testSuccess.getSuccess(), "testSuccess fail");
logger.info("testSuccess: {}", JSON.toJSONString(testSuccess));
}
}
➮ 2-3.提高单元测试覆盖率
使用idea自带的单元测试覆盖率工具可以查看相应的覆盖率。 绿色的条代表已覆盖,红色的条代表未覆盖。
以下是单元测试的覆盖率文档,分别是类覆盖率、方法覆盖率、行覆盖率,从图中可以看出我们的行覆盖率只有64%,还有提升的空间。
如何提升呢?答案就是 mock。 先上改造后的代码。
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = CommonTestApplication.class)
public class CommonEntityServiceTest {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Autowired
private CommonEntityService commonEntityService;
@Autowired
private CommonMockFactory commonMockFactory;
@Test
public void test() {
Mockito.when(commonMockFactory.webRpc.get()).thenReturn(ApiResult.success("mock result 1"));
Mockito.when(commonMockFactory.webRpc.get2("test")).thenReturn(ApiResult.success("mock result 2"));
ApiResult<Void> testSuccess = commonEntityService.test(new CommonEntity());
Assert.isTrue(testSuccess.getSuccess(), "testSuccess fail");
logger.info("testSuccess: {}", JSON.toJSONString(testSuccess));
}
@Test
public void testWithMock() {
Mockito.when(commonMockFactory.webRpc.get()).thenReturn(ApiResult.success("mock result 1"));
Mockito.when(commonMockFactory.webRpc.get2("test")).thenReturn(ApiResult.success("mock result 2"));
ApiResult<Void> testSuccess = commonEntityService.test(new CommonEntity());
Assert.isTrue(testSuccess.getSuccess(), "testSuccess fail");
logger.info("testSuccess: {}", JSON.toJSONString(testSuccess));
// 模拟 webRpc.get() 失败
Mockito.when(commonMockFactory.webRpc.get()).thenReturn(ApiResult.error(BizRespStatusEnum.ILLEGAL_PARAM));
Mockito.when(commonMockFactory.webRpc.get2("test")).thenReturn(ApiResult.success("mock result 2"));
ApiResult<Void> testFail1 = commonEntityService.test(new CommonEntity());
Assert.isTrue(!testFail1.getSuccess(), "testFail1 fail");
logger.info("testFail1: {}", JSON.toJSONString(testFail1));
Mockito.when(commonMockFactory.webRpc.get()).thenReturn(ApiResult.success("mock result 1"));
// 模拟 webRpc.get2() 失败
Mockito.when(commonMockFactory.webRpc.get2("test")).thenReturn(ApiResult.error(BizRespStatusEnum.ILLEGAL_PARAM));
ApiResult<Void> testFail2 = commonEntityService.test(new CommonEntity());
Assert.isTrue(!testFail2.getSuccess(), "testFail1 fail");
logger.info("testFail2: {}", JSON.toJSONString(testFail2));
Mockito.when(commonMockFactory.webRpc.get()).thenReturn(ApiResult.success("mock result 1"));
Mockito.when(commonMockFactory.webRpc.get2("test")).thenReturn(ApiResult.success("mock result 2"));
try (MockedStatic<RmiUtil> rmiUtilMockedStatic = Mockito.mockStatic(RmiUtil.class)) {
// 模拟 RmiUtil.getRemoteResult() 失败
rmiUtilMockedStatic.when(RmiUtil::getRemoteResult).thenReturn(Optional.empty());
ApiResult<Void> testFail3 = commonEntityService.test(new CommonEntity());
Assert.isTrue(!testFail3.getSuccess(), "testFail3 fail");
logger.info("testFail3: {}", JSON.toJSONString(testFail3));
}
}
}
单元测试的执行结果。
2022-05-21 23:23:46.516 INFO 35136 --- [ main] c.p.j.s.c.c.s.i.CommonEntityServiceImpl : insert 0 common entity
2022-05-21 23:23:46.589 INFO 35136 --- [ main] c.p.j.s.c.c.s.CommonEntityServiceTest : testSuccess: {"code":"200","msg":"调用成功","success":true}
2022-05-21 23:23:46.590 INFO 35136 --- [ main] c.p.j.s.c.c.s.i.CommonEntityServiceImpl : getRpc fail: ApiResult{success=false, code='400', msg='参数异常', result=null}
2022-05-21 23:23:46.590 INFO 35136 --- [ main] c.p.j.s.c.c.s.CommonEntityServiceTest : testFail1: {"code":"400","msg":"参数异常","success":false}
2022-05-21 23:23:46.591 INFO 35136 --- [ main] c.p.j.s.c.c.s.i.CommonEntityServiceImpl : getRpc2 fail: ApiResult{success=false, code='400', msg='参数异常', result=null}
2022-05-21 23:23:46.591 INFO 35136 --- [ main] c.p.j.s.c.c.s.CommonEntityServiceTest : testFail2: {"code":"400","msg":"参数异常","success":false}
2022-05-21 23:23:46.629 INFO 35136 --- [ main] c.p.j.s.c.c.s.i.CommonEntityServiceImpl : getRemoteResult fail
2022-05-21 23:23:46.629 INFO 35136 --- [ main] c.p.j.s.c.c.s.CommonEntityServiceTest : testFail3: {"code":"002","msg":"系统异常","success":false}
再来看看改造之后的覆盖率!从下图中可以看出单元测试的行覆盖率达到了100%,惊不惊喜,意不意外!
3.总结
在我们没用 mock 工具时,别说覆盖率了,执行一个单元测试都很麻烦。 使用 mock 工具之后,我们不仅可以很方便的执行单元测试,还能使用各种奇技淫巧来提升行覆盖率,强烈推荐! 写好单元测试一点都不简单,本文只是拿了一个简单的场景来举例,在单元测试的行覆盖率达到100%时,代码量就已经是源码的两倍还多了,害!但是 bug 和 单元测试 总要选一个的,看大家的选择了。
➮ 了解更多敏捷开发、项目管理、行业动态等消息,关注我们的团队博客或点击 LigaAI-智能研发协作平台,在线申请体验我们的产品。
